ApisCP provides a variety of means to customize your environment. Each service is different and the means to configure it varies. Many services have files that are verboten, don't touch under any circumstance. They are periodically overwritten and the primary means to ensure what you run is what is developed.
CP_ROOT is the panel home, typically either /usr/local/apnscp or /usr/local/apiscp.
# Apache
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Customization file: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd-custom.conf
Additionally, module configuration may be inserted in /etc/httpd/conf.d to load or modify existing modules. Per-site configuration is located in /etc/httpd/conf/siteXX or /etc/httpd/conf/siteXX.ssl for SSL-specific context. By convention customizations are placed in a file named custom in these directories. To get the site ID of a domain use the helper command, get_site_id.
After making changes, htrebuild will compile Apache's modular configuration followed by systemctl reload httpd to reload the web server.
# Placeholder page
A placeholder page is created whenever an account, addon domain, or subdomain is created. Placeholders are always named "index.html" and reside in the respective document root (opens new window). Content is generated from a Blade file, which allows for customization prior to rendering of the placeholder.
Copy /usr/local/apnscp/resources/templates/apache/placeholder.blade.php to /usr/local/apnscp/config/custom/resources/templates/apache/placeholder.blade.php creating parent directories as needed. index.html may not be updated once written.
# Suspension page
All suspended accounts via SuspendDomain redirect to /var/www/html/suspended.html. A suspension page is not provided by default in ApisCP but may be created by the admin. Suspension rules may be modified by adjusting the rewrite rules.
Copy /usr/local/apnscp/resources/templates/apache/suspend-rules.blade.php to /usr/local/apnscp/config/custom/resources/templates/apache/suspend-rules.blade.php creating parent directories as needed.
A site once suspended will compile these rules into /etc/httpd/conf/siteXX/00-suspend. Rules will not be updated unless suspended again. admin:collect() provides a convenient way to do this.
yum install -y jq
cpcmd -o json admin:collect '[]' '[active:false]' | jq -r 'keys[]' | while read -r SITE ; do SuspendDomain $SITE ; done
# Additional VirtualHost contexts
All VirtualHost containers should be managed directly by ApisCP within /etc/httpd/conf/virtual and backed by a real account. If additional VirtualHost containers are necessary, they may be located under httpd-custom.conf or /etc/httpd/conf.d. VirtualHost contexts located under httpd-custom.conf must match the ServerName value of the server hostname (net.hostname Scope).
# Evasive
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: n/a
Customization file: /etc/httpd/conf.d/evasive.conf or httpd-custom.conf
Alternatively consider the apache.evasive Scope, which provides error checking.
# mod_security
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/httpd/conf.d/mod_security.conf
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/httpd/modsecurity.d/activated_rules/clamav.conf
Customization file: /etc/httpd/modsecurity.d/ or httpd-custom.conf
# PageSpeed
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/httpd/conf.d/pagespeed.conf MANAGED BLOCK (#BEGIN/#END)
Customization file: /etc/httpd/conf.d/pagespeed.conf or httpd-custom.conf
# ApisCP
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /usr/local/apnscp/config/*
Customization file: /usr/local/apnscp/config/custom/*
ApisCP supports overriding views, apps, modules, and configuration. Modification is covered in detail in PROGRAMMING.md.
TIP
ApisCP was originally called APNSCP. Internally, in many places, the panel is still referred to as APNSCP. ApisCP is a bit easier to pronounce.
# View overrides
All views may be copied into CP_ROOT/config/custom/resources/views/<path> from CP_ROOT/config/custom/resources/views/<path>. Custom views take precedence, including all mail templates. Overriding layout.blade.php allows customization to the skeleton of all apps in ApisCP.
Updating configuration first time
ApisCP compiles configuration on each start to provide the best possible performance. When creating resource overrides in CP_ROOT/config/custom/resources/view or CP_ROOT/config/custom/resources/templates the first time restart ApisCP so it knows to look in these directories. Prior to making this change, these locations are compiled out on boot.
systemctl restart apiscp
# Layout
A master layout named "layout" is provided in CP_ROOT/config/custom/resources/views/. As with all templates suffixed "blade.php", it utilizes Blade (opens new window). A theme-specific blade may override the master layout by creating an eponymous template in CP_ROOT/config/custom/resources/views/. For example, to override the "apnscp" theme, create a file named CP_ROOT/config/custom/resources/views/apnscp.blade.php. Inheritance is supported via @extends("layout") in addition to section injection.
# App overrides
Apps may be completely overridden or on a file-per-file basis (such as replacing application.yml).
To override the app entirely, copy it from CP_ROOT/apps/<name> to CP_ROOT/config/custom/apps/<name>. To override a specific file, create the corresponding directory structure in CP_ROOT/config/custom/apps/<name>, then copy the file over.
Role menus, i.e. what is loaded when a corresponding user type logs in (admin, site, user) may be overridden as well. Menus are based on code under lib/html/templateconfig-<role>.php. Additional includes may be located under CP_ROOT/config/custom/templates/<role>.php. This is a sample extension for ApisCP when a billing module is configured to allow clients direct access to manage billing:
CP_ROOT/config/custom/templates/site.php:
<?php
$templateClass->create_link(
'Billing History', /* application title */
'/apps/billinghistory', /* application URL */
cmd('billing_configured'), /* conditions to show application */
null, /* optional application icon */
'account' /* optional category name */
);
$templateClass->create_link(
'Change Billing',
'/apps/changebilling',
cmd('billing_configured'),
null,
'account'
);
$templateClass->create_link(
'Client Referrals',
'/apps/referrals',
cmd('billing_configured'),
null,
'account'
);
# Onboarding tours
New in 3.2.22
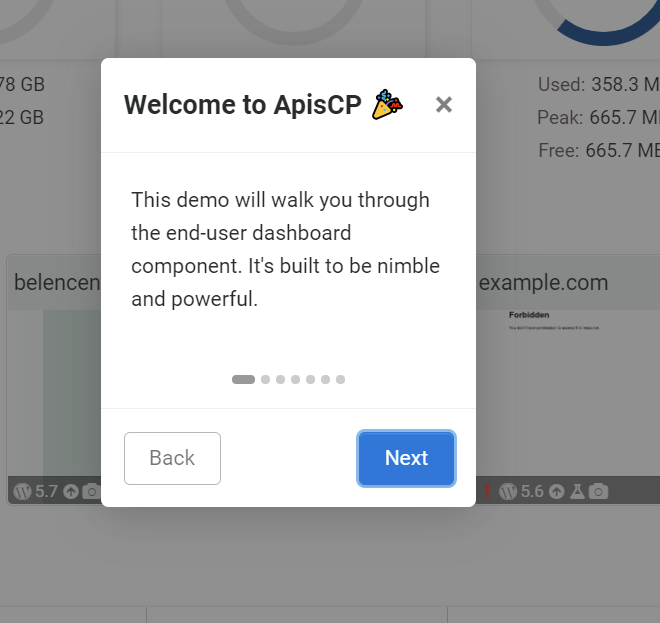
Users may be introduced to a brief demo on the first app view or on demand when \Page_Renderer::show_tutorial(); is called (see CP_ROOT/config/custom/apps/template/template.php for sample invocation). Steps are loaded from application.yml bundled in CP_ROOT/config/custom/apps/APP NAME/. As with all application data, this file may be individually overridden by copying apps/APP NAME/application.yml to CP_ROOT/config/custom/apps/APP NAME/application.yml.
application.yml does not support inheritance; thus, the overrode file is what is used for application metadata. Parsed metadata remains cached for 24 hours unless the panel is in debug mode.
# Sample tour data from dashboard/application.yml
tour:
- title: "Welcome to {{ PANEL_BRAND }} 🎉"
content: "This demo will walk you through the end-user dashboard component. It's built to be nimble and powerful."
- selector: '.usage-gauges > div'
title: "Resource usage"
content: "A variety of metrics relating to resource consumption lets you know how much you've used."
- selector: '#cpu-gauge'
title: "CPU usage"
content: "CPU resets every 24 hours measuring both system and user time."
when: "{{ !\\UCard::get()->is('admin') }}"
- selector: "#rampartMarker"
title: "Firewall"
content: >-
Firewall stats are available within the dashboard. See <a class='ui-action-label ui-action-visit-site-tab ui-action'
target='apiscp-docs' href='https://docs.apiscp.com/FIREWALL'>FIREWALL.md</a> for advanced usage.
when: "{{ \\UCard::get()->is('admin') }}"
tour contains all onboarding steps. Each step may optionally present a title field that sets the modal title, an optional selector highlights callouts. content is required. when must evaluate to a truthy condition (1, "1", "true", true, "non-empty string") to display. All fields support Blade templating.
Evaluation at page load
Onboarding binds to the DOM at page load. Any elements replaced after page load will not receive callout treatment.
# Hiding/removing existing apps
Apps populated as part of ApisCP may be hidden or removed from view using hide() and remove() respectively. Application ID is the basename from the URI path, i.e. for /apps/foo the application ID is "foo" and likewise "quuz" is the application ID for /apps/quuz.
CP_ROOT/config/custom/templates/admin.php:
<?php
// remove Nexus app from admin
$templateClass->getApplicationFromId('nexus')->remove();
// allow Dashboard access, but remove from side menu
$templateClass->getApplicationFromId('dashboard')->hide();
// remove "foo" app. Note if this does not exist it is a no-op
$templateClass->getApplicationFromId('foo')->hide();
// alternatively to check if "foo" exists
if ($templateClass->getApplicationFromId('foo')->exists()) {
// do something
}
# Menu reset
New in 3.2.18
When working with custom configurations, it may be desired to reset all menu items. clear() empties all menu and statistics.
<?php
$templateClass->clear();
// Enable only the Dashboard
$templateClass->create_link(
'Dashboard',
'/apps/dashboard',
true,
null,
''
);
Dashboard required
/apps/dashboard must be a valid URI in all menus as this serves as the default destination after login. This may be changed by modifying the entry app below. Once changed, it's no longer necessary to include the "Dashboard" app.
# Plan-specific menu
New in 3.2.18
Per-plan menus may be used following the naming scheme ROLE-PLAN. For example, to use a custom menu layout for the plan "dns-only" that applies to Site Administrators, create the following file CP_ROOT/config/custom/templates/site-dns-only.php. If found, this menu will be used instead of CP_ROOT/custom/templates/site.php.
Plan-specific menus behave otherwise the same as a custom menu. To clear all menu items use clear().
<?php
$templateClass->clear();
// create a DNS-only layout
$templateClass->create_link(
'Dashboard',
'/apps/dashboard',
true,
null,
''
);
$templateClass->create_link(
'DNS Manager',
'/apps/dns',
true,
null,
''
);
# Changing entry app
New in 3.2.28
setEntryApp() allows you to change the entry app on successful login. By default, the value is dashboard, which corresponds to the Dashboard app accessed through /apps/dashboard.
<?php
$templateClass->clear();
// create a pure DNS-only layout
$templateClass->setEntryApp('dns');
$templateClass->create_link(
'DNS Manager',
'/apps/dns',
true,
null,
''
);
# App view overrides
Any app that uses Blade templates (views/ directory) is eligible to override components of the template structure. Create the same structure in config/custom/apps/<name> as is in apps/<name>. For example to override CP_ROOT/config/custom/apps/ssl/views/partials/certificate-detected.blade.php, copy that file to CP_ROOT/config/custom/apps/ssl/views/partials/certificate-detected.blade.php. ApisCP will load the view from this location first. It is advisable to copy the entire application over (App overrides) as application structure may change between releases.
# Web App overrides
Web Apps use a different set of locations for overrides. An app may be overrode by cloning the git repository (opens new window) into CP_ROOT/config/custom/ (see README.md bundled with each Web App) or by copying the respective file into CP_ROOT/config/custom/webapps/APP-NAME/views. For example, to override the options-install.blade.php template bundled with WordPress, the path would be CP_ROOT/config/custom/webapps/wordpress/views/options-install.blade.php.
# Global constants
Constants may be overrode or added to global scope via CP_ROOT/config/custom/constants.php:
<?php
return [
'BILLING_HOST_READ' => $dbyaml['billing']['read']['host'],
'BILLING_HOST_WRITE' => $dbyaml['billing']['write']['host'],
'BILLING_USER' => $dbyaml['billing']['read']['user'],
'BILLING_PASSWORD' => $dbyaml['billing']['read']['password'],
'BILLING_DB' => $dbyaml['billing']['read']['database'],
'BILLING_HOST_BACKUP' => $dbyaml['billing']['backup']['host'],
];
# DNS template overrides
DNS is generated from a base template in CP_ROOT/config/custom/resources/templates/dns. Presently mail and dns templates are supported. For each template to override copy the respective template to CP_ROOT/config/custom/resources/templates/dns/. Validate DNS template consistency via cpcmd dns:validate-template TEMPLATENAME.
# Themes
New themes may be created and placed under CP_ROOT/public/css/themes and CP_ROOT/public/images/themes. The default theme may be changed with cpcmd:
cpcmd scope:set cp.config style theme newtheme
Per theme layouts may be set following the layout override mentioned above.
# Building themes
Grunt is used to build themes from the SDK (opens new window). Some Sass (opens new window) knowledge is recommended. Bootstrap (opens new window) is also helpful to know but simple enough to learn as you go along. ApisCP is presently based on Bootstrap 4.0.
git clone https://github.com/apisnetworks/apnscp-bootstrap-sdk
pushd apnscp-bootstrap-sdk
npm install
env THEME=apnscp grunt watch
Now changes may be made to the "apnscp" theme in scss/themes/apnscp. It will also be necessary to put either the panel in debug mode using the cp.debug scope or by flagging the session as debug. Session is encoded in the browser session as session.id. Use this value with misc:debug-session to selectively enable debugging for this session:
# Enable debugging on session LETceXuAZ9p1MW0yPd7n1b3Btk9t9Weh
env DEBUG=1 misc:debug-session LETceXuAZ9p1MW0yPd7n1b3Btk9t9Weh
It's recommended to create a new theme by copying one of the existing themes. Default theme may be changed using cpcmd scope:set cp.config style theme NEWTHEME. Likewise run env THEME=NEWTHEME grunt to build a minified release of the theme prior to shipment. Debug sessions source non-minified assets.
# ApisCP configuration
All configuration must be made to CP_ROOT/config/custom/config.ini. cpcmd provides a short-hand tool to edit this file.
# Show all configuration
cpcmd scope:get cp.config
# Set configuration
cpcmd scope:set cp.config core fast_init true
Refer to config.ini (opens new window) that ships with ApisCP for a list of configurables.
# HTTP configuration
All changes may be made to CP_ROOT/config/httpd-custom.conf. After changing, restart ApisCP, systemctl restart apiscp
# ClamAV
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/clamd.conf, /etc/clamd.d/scan.conf MANAGED BLOCK (#BEGIN/#END)
Customization file: /etc/clamd.d/scan.conf
In addition to writing directly to the configuration file, several configurations support custom blocks. All custom variables are named clamav_VAR__custom where VAR corresponds to the following variables.
| Variable | Overrides |
|---|---|
| clamd_config | /etc/clamd.d/scan.conf |
| clamd_daemon_systemd | /etc/systemd/system/clamd@scan.service.d/override.conf |
| clamd_exclude_path | "ExcludePath" directive in /etc/clamd.d/scan.conf |
| db_update_command_options | Additional argv to freshclam command |
| freshclam_config | /etc/freshclam.conf |
| scan_command_options | Addtional argv to clamdscan command |
For example, to disable ConcurrentDatabaseReload in clamd:
cpcmd scope:set cp.bootstrapper clamav_clamd_config__custom "ConcurrentDatabaseReload yes"
# Update ClamAV
upcp -sb clamav/setup
Note each directive must be delimited by a newline. One trick to do this is use echo -e to evaluate metacharacters, including the newline character \n.
cpcmd scope:set cp.bootstrapper clamav_clamd_config__custom "$(echo -e "ConcurrentDatabaseReload yes\nDirective2 yes")"
# Dovecot
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/dovecot/conf.d/apnscp.conf
Customization file: /etc/dovecot/local.conf
A few conflicting files in /etc/dovecot/conf.d are wiped as part of Bootstrapper (opens new window). These files will always be removed if found:
- 10-auth.conf
- 10-mail.conf
# fail2ban
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/fail2ban/*.conf
Customization file: /etc/fail2ban/*.local, /etc/fail2ban/jail.d
Any file in fail2ban may be overridden with a corresponding .local file. It takes the same name as the source file, except it ends in .local instead of .conf.
See also
- MANUAL 0.8 (opens new window) (fail2ban.org) - covers configuration/override in detail
# haproxy
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
Customization file: /etc/haproxy/conf.d/*
# MySQL
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/my.cnf.d/apnscp.conf
Customization file: /etc/my.cnf.d/*
Additionally, configuration may be overrode in Bootstrapper using mysql_custom_config. These values are set in /etc/my.cnf.d/apnscp.cnf and may be substituted in lieu of a higher order override.
Create a special variable named mysql_custom_config in /root/apnscp-vars-runtime.yml. This is a dict that accepts any number of MySQL server directives that takes precedence.
Sample
mysql_custom_config:
# Disable max_join_size protection
max_join_size: -1
Then run upcp -sb mysql/install to update configuration.
# phpMyAdmin
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /var/www/html/phpMyAdmin/config.inc.php
Customization file: /var/www/html/phpMyAdmin/config.local.inc.php
Create this customization file if it does not already exist.
<?php
// set custom configuration here
?>
# Postfix
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/postfix/master.conf
Customization file: /etc/postfix/main.cf, /etc/postfix/master.d, postfix_custom_config var
Postfix does not provide a robust interface to extend its configuration. /etc/postfix/master.cf, which is the service definition for Postfix, may not be updated as it is replaced with package updates (opens new window).
Pay special adherence to configuration variables (opens new window) in Bootstrapper. These are always overwritten during integrity check. To override these variables, create a special variable named postfix_custom_config in /root/apnscp-vars-runtime.yml. This is a dict that accepts any number of Postfix directives that takes precedence.
Sample
postfix_custom_config:
disable_vrfy_command: no
vmaildrop_destination_rate_delay: 15
postfix_custom_master_config works similarly to postfix_custom_config except it is a string applied to /etc/postfix/master.cf. Additionally, per-site configurations, such as transports, may be added in /etc/postfix/master.d. Configuration must end in .cf. Any file prefixed with siteXX- is considered affiliated with the designated site and will be removed on site deletion.
Do not assume these templates will be capable of Jinja templating in Ansible. Instead, the template must be statically generated at account creation/edit.
Sample
# Add SPF checking service, note this is for illustrative purposes and
# largely obviated by SpamAssassin and rspamd spam filters
postfix_custom_master_config: |-
policyd-spf unix - n n - 0 spawn
user=policyd-spf argv=/usr/bin/policyd-spf
Sample
# In /etc/postfix/master.d/site12.cf
# Add a custom smtp transport
mydomain.com-out unix - - n - - smtp
-o smtp_helo_name=mydomain.com
-o smtp_bind_address=64.22.68.2
Then to merge changes for both examples, run upcp -sb mail/configure-postfix.
# PostgreSQL
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: n/a
Customization file: /var/lib/pgsql/<ver number>/conf/postgresql.auto.conf, pgsql_custom_config var
Configuration variables (opens new window) in Bootstrapper allow for overrides in postgresql.conf. To override these variables, create a special variable named pgsql_custom_config in /root/apnscp-vars-runtime.yml. This is a dictionary that accepts any number of PostgreSQL directives that takes precedence.
Sample
pgsql_custom_config:
max_connections: 100
track_io_timing: on
Run upcp -sb pgsql/install after setting overrides to apply to postgresql.conf.
postgresql.auto.conf (opens new window) is modified by SQL queries such as SET max_connections TO 100;. Values within here take precedence over postgresql.conf directives and will not be overridden by Bootstrapper.
# PHP
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/php.ini MANAGED BLOCK (# BEGIN/# END)
Customization file: /etc/phpXX.d/*
ApisCP uses a managed block in /etc/php.ini. Any directives within this block will always be overwritten. To override any values within this block, make changes in /etc/phpXX.d/ where XX is the version major/minor of PHP. Note this affects global PHP settings. To change settings per site look into php_value (opens new window) in either .htaccess or siteXX/custom mentioned above in Apache.
# rspamd
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/rspamd/local.d/*
Customization file: /etc/rspamd/override.d/*
For each file in local.d to override create a corresponding file in override.d/. This follows either UCL (opens new window) or JSON. When working with JSON, drop the leading + closing braces ("{", "}"). This is due to a parsing quirk of rspamd. An example (opens new window) of reconstituting to valid JSON is available in the Github repository.
Additionally rspamd Playbook variables may be overrode in a similar manner to Postfix. In /root/apnscp-vars.yml add:
rspamd_neural_custom_config:
enabled: false
rspamd_actions_custom_config:
add_header: 20
rspamd provides many configurables that don't require a direct override. Neural module for example is also conditionally enabled using rspamd_enable_neural_training. Be sure to refer back to defaults (opens new window) in mail/rspamd.
# SpamAssassin
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: n/a
Customization file: /etc/mail/spamassassin/local.cf
# SSH
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/ssh/sshd_config MANAGED BLOCK (# BEGIN/# END)
Customization file: /etc/ssh/sshd_config
sshd_config may be modified. Do not edit the directives within # BEGIN ApisCP MANAGED BLOCK and # END ApisCP MANAGED BLOCK. Port and public key authentication may be modified with Scopes,
# Enable ssh daemon ports 22 and 58712
cpcmd config:set system.sshd-port '[58712,22]'
# Disallow password-based logins, public key only
cpcmd config:set system.sshd-pubkey-only true
# vsftpd
⚠️ DO NOT TOUCH: /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
Customization file: vsftpd_custom_config var
vsftpd does not provide a robust interface to extend its configuration. Configuration is written as part of vsftpd/configure (opens new window) role in Bootstrapper. Boolean values are unconverted, so "NO" and "YES" must be specified as string literals by surrounding with quotes. Configuration may be located in /root/apnscp-vars-runtime.yml. Run upcp -sb vsftpd/configure to commit changes.
Sample
vsftpd_custom_config:
log_ftp_protocol: "YES"
pasv_address: "1.2.3.4"
hide_ids: "NO"
