# PHP-FPM
PHP-FPM is a high performance PHP daemon built on FastCGI and introduced in ApisCP 3.1. On ApisCP platforms PHP-FPM demonstrates a 2-3x higher throughput than mod_php ("ISAPI"), which integrates into Apache as a module. In PHP-FPM, a request is sent over a UNIX domain socket to a dedicated worker pool for processing. In ISAPI, PHP requests are handled by a separate VM integrated into Apache that must scaffold and tear down at the end of each request. ISAPI is ideal in low-memory environments but loses relevance outside the niche scenario.
PHP-FPM offers several advantages over an ISAPI integration:
# Advantages
Resource enforcement PHP-FPM pools run under the group ID of each account, which affords simple cgroup (opens new window) treatment to each process. ISAPI runs in a threaded environment that is incompatible with cgroup v1 (cgroup v2 supports threaded accounting at the cost of immense complexity). Every request that comes through may be governed by CPU, memory, block IO, and network IO limits. Likewise every request may be accounted towards an account's cumulative usage.
Jailing Pools run within the synthetic root of each account ensuring isolation between accounts. ISAPI uses a variety of mechanisms to impede arbitrary access (SECURITY.md) that may provide a loose deterrent. PHP-FPM requests are jailed using systemd namespaces (opens new window), a powerful OS feature that is part of userland management (PID 1).
To limit snooping or the potential of socket remaps, sockets are stored outside the synthetic root in a general runtime directory that inhibits access beyond directory access using conventional discretionary access controls.
Path cache Running each account in a jail obviates the requirement for open_basedir restrictions. open_basedir restrictions disable realpath caching (bug #52312 (opens new window)) to stymie symlink attacks. Enabling realpath caches improves throughput by caching filesystem metadata and making assumptions about the properties of the file.
User customization As each pool runs independent of other accounts, end-users may tailor the PHP pool to their needs, such as changing the process manager or PHP settings without relying on .htaccess directives that are always re-evaluated on each request. Users cannot tune critical values such as the pool user, chroot, socket path (without grave consequence) or other protected values as these are extracted to the systemd service definition.
cgroup enforcement is strongly encouraged to prevent abuse. Set
cgroup,memoryas a minimum to ensure that a user cannot define a static pool that could spawn an egregious number of workers to cause an out-of-memory condition.Multi-tenancy PENDING Users may spawn multiple PHP-FPM pools each with different users. For example, it would be possible to create a PHP pool for production and staging in which the production environment adheres to the principles of Fortification and the staging environment is owned entirely by the developer account; both operate under different UIDs.
cgroup enforcement is strongly encouraged to prevent abuse. Set
cgroup,memoryas a minimum to ensure that a user cannot define a static pool that could spawn an egregious number of workers to cause an out-of-memory condition.Flexible ownership Similarly, each pool may operate under a different UID, preferably a system user without machine access, to provide further separation between accounts and ensure zero overlap when discretionary access controls are applied. Setting the pool to the account owner facilitates easy management without the need for Fortification but also negates any benefits of audit trails should an account get hacked from an insecure WordPress plugin or any PHP application.
# Disadvantages
Memory requirements Each pool requires a minimum of 40 MB. In real-world situations each additional worker may require an additional 16-24 MB memory in typical usage scenarios. Workers that spawn from the pool manager follow copy-on-write (opens new window) semantics idiosyncratic of a fork() (opens new window) syscall, meaning the address space for PHP is shared when a worker spawns. Only the PHP scripts loaded within the worker are allocated additional memory.
To help ameliorate memory constraints in high density environments, PHP-FPM uses the ondemand (opens new window) process manager to automatically sleep idle processes after a set time (1 minute). This can be overrode by changing the PHP-FPM configuration template (opens new window). ondemand exhibits a very low latency when used in conjunction with OPCache (enabled by default) to spin up additional workers.
# Architecture
All PHP-FPM pools are managed through systemd using socket activation. When a request is received by Apache, it writes to a Unix domain socket, outside the account chroot, managed by systemd. systemd spawns the worker pool to handle subsequent requests, which solves the Thundering herd problem (opens new window) to a certain extent. Each request is jailed to the account through systemd. cgroup assignment is done prior to pool initialization, which extends to all child processes spawned from within the pool ensuring fair resource treatment. Configuration may be overriden on a per-pool level with pool configuration at the discretion of (and of consequence to) the account owner.
# Building
# Configuration
The default PHP interpreter may be changed using the apache.php-version Scope. Additional configuration flags may be specified by setting phpXX_build_flags in Bootstrapper where XX is <MAJOR><MINOR> (cp.bootstrapperis a Scope to facilitate interaction). Alternatively php_build_flags may be set, which applies to all PHP builds.
# Enable PCNTL extension, signal and process handling for use with Laravel Horizon
# Assuming PHP 7.4 is installed, configuration will apply to this build.
cpcmd scope:set cp.bootstrapper php74_build_flags "--enable-pcntl"
# Force rebuild. This implicitly sends php_force_build=true to bootstrap.yml
cpcmd scope:set apache.php-version 7.4
# Installing modules
To install imagick off PECL for the system PHP build,
upcp -sb --var="pecl_extensions=imagick" php/install-extensions
TIP
--var=force_module_rebuild=true may be specified to force a module update as well as module configuration in FST/siteinfo/etc/phpXX.d/.
Modules may be set per version and permanently applied for all PHP builds by setting either pecl_phpXX or pecl_extensions variables.
# Always build imagick + igbinary + redis extensions
cpcmd scope:set cp.bootstrapper pecl_extensions '[imagick,igbinary,redis]'
# Build all modules
upcp -sb php/install-extensions
# Non-PECL modules
git and archive sources are also supported. If we want to add mailparse (from PECL), memcached (from GitHub), and inotify:
cpcmd scope:set cp.bootstrapper pecl_extensions '["mailparse","https://github.com/php-memcached-dev/php-memcached.git","https://pecl.php.net/get/inotify-2.0.0.tgz"]'
upcp -sb php/install-extensions
DANGER
This task runs as root. Be sure you trust module sources.
By convention ApisCP will use the basename up to the first character in the set :-. as the module name. In the above example, php-memcached module configuration would be saved as "php.ini" in FST/siteinfo/etc/phpXX.d/. You can override this behavior using dense extension format.
# Dense extension format
Not all extensions are named as you'd want them to be. ApisCP supports a dense format for extensions that explicitly defines the extension URL, name, and whether it's a Zend extension. An example of this is Xdebug that when installed from the latest GitHub release would be treated as "2.ini".
upcp -sb --var=pecl_extensions='{"name":"xdebug","zend":true,"extension":"https://github.com/xdebug/xdebug/archive/2.9.6.tar.gz"}' php/install-extensions apnscp/php-filesystem-template
Dense mode accepts the following attributes:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| name | Extension name |
| zend | Whether Zend extension |
| extension | Standard extension URI (PECL, URL, local file) |
| flags | Flags to pass to configure script |
| version | Specific version to install. git, PECL URIs only |
Likewise to set as default for all PHP builds,
cpcmd scope:set cp.bootstrapper pecl_extensions '["mailparse","https://github.com/php-memcached-dev/php-memcached.git","https://pecl.php.net/get/inotify-2.0.0.tgz",'\''{"name":"xdebug","zend":true,"extension":"https://github.com/xdebug/xdebug/archive/2.9.6.tar.gz"}'\'']'
Quote parsing
Escaping quotes can become elaborate very quickly. To escape a nested single quote, first close the quote, then escape the intended quote, then resume single quotes. Adding ' inside '...' would thus be ''\'''
# Enabling sites
Switching an account over is a breeze! Flip the apache,jail setting to enable jailing:
EditDomain -c apache,jail=1 -D domain.com
To set the default going forward, either make the adjustment in a plan via ./artisan opcenter:plan or set the default FPM behavior, cpcmd scope:set cp.config httpd use_fpm true. All new accounts created will use PHP-FPM by default.
To perform an en-masse edit:
cd /home/virtual
EditDomain --all -c apache,jail=1
And for the overachieving variety:
yum install -y jq
cpcmd -o json admin:collect null '[apache.jail:0]' | jq -r 'keys[]' | while read -r SITE ; do
echo "Editing $(get_config "$SITE" siteinfo domain)"
EditDomain -c apache,jail=1 "$SITE"
done
There will be an elision delay configured in [httpd] => reload_delay designed to allow multiple HTTP reload calls to merge into a single call to prevent a denial of service attack. By default, this is 2 minutes.
# Single-user behavior
ApisCP supports a single-user behavior which disables the benefits of Fortification. This behavior is consistent with cPanel and competing panels that do not isolate web users. Set apache,webuser to match the account admin:
EditDomain -c apache,webuser=myadmin -D mydomain.com
# Or for simplicity...
EditDomain -c apache,webuser="$(get_config mydomain.com siteinfo admin_user)" -D mydomain.com
ApisCP will change ownership on all files matching the previous user ("apache") to the new user "myadmin". Ownership change from a system user to an account user is an irreversible process. Now, files created by the web server will be under the account username. Should and weakness exist in any web app on the account that allows an attacker to run arbitrary code, then the attacker now has unrestricted access to all users on the account.
This is an extremely dangerous configuration that should be avoided at all costs.
# Service management
Worker throughput may be examined via systemd. FPM workers are watchdog-aware, which means they automatically report health back to systemd within a deadline window to improve reliability, recovering as needed. Worker metrics may be examined via systemctl status,
systemctl status php-fpm-site1-domain.com
PHP-FPM workers are grouped <SITE>-<MARKER>. By default the marker is the primary domain on the account. site is the immutable siteXX designator of the domain.
systemctl status php-fpm-site1-domain.com
#########################
# Sample response follows
#########################
● php-fpm-site1-domain.com.service - PHP worker for site1 - domain.com
Loaded: loaded (/usr/local/apnscp/resources/templates/apache/php/fpm-service.blade.php; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2019-08-30 17:35:01 EDT; 1min 25s ago
Process: 17905 ExecStartPost=/bin/sh -c for i in /sys/fs/cgroup/*/site1/tasks ; do echo $MAINPID > $i ; done (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 17898 (php-fpm)
Status: "Processes active: 0, idle: 1, Requests: 3, slow: 0, Traffic: 0.0667req/sec"
Tasks: 1
Memory: 26.0M
CGroup: /system.slice/php-fpm-site1-domain.com.service
├─17898 php-fpm: master process (/etc/php-fpm.d/sites/domain.com.conf)
└─17906 php-fpm: pool domain.com
ApisCP manages pool groups, restarting as needed after the elision window expires. To restart or suspend the pool for a site, use the php-fpm-siteXX service wrapper.
# Suspend all pools allocated to site1
# Note: socket activation will start the worker on demand!
systemctl stop php-fpm-site1
# Restart all PHP-FPM pools, for example configuration updated
systemctl restart php-fpm-site1
Permanent suspension may be achieved by disabling the corresponding socket,
systemctl mask php-fpm-site1-*.socket
systemctl stop php-fpm-site1
However this is seldom useful as suspending the account achieves a similar result:
SuspendDomain site1
# Bulk update
php-fpm is a composite unit to manage all PHP-FPM instances on a server. For example, it may be necessary to propagate configuration changes from a lower filesystem layer.
# Make changes in FST/siteinfo/...
systemctl stop php-fpm
systemctl reload fsmount
systemctl start php-fpm
# Service relationship
Both php-fpm and php-fpm-siteXX represent one-way bindings to the respective pools. The full service name, php-fpm-siteXX-domain consists of 2 parts, a socket-activated service ending in .socket that spawns the PHP-FPM pool that shares the same name once activity arrives on that socket from Apache.
Restarting php-fpm.service will restart all PHP-FPM pools previously running, however, will leave dormant pools inactive. Likewise the same treatment is applied to php-fpm-siteXX.service but only to pools belonging to that site. Restarting php-fpm-siteXX-domain.socket will restart the similarly named service if it was previously listening or re-enable the socket listener if previously deactivated via a stop command (systemctl stop php-fpm). Starting php-fpm-siteXX-domain.service will unconditionally start the PHP-FPM pool without waiting for activity from the named .socket.
# Overriding service definitions
Overriding configuration follows systemd convention (opens new window). Create a directory in /etc/systemd/system/ named after the service. Any .conf within the directory will be merged into the service definition thus making it possible, for example, to change the PHP-FPM worker or set environment variables prior to pool startup. Further, overrides are non-destructive and guaranteed to not be overwritten.
cd /etc/systemd/system
mkdir php-fpm-site1-example.com.service.d/
cd php-fpm-site1-example.com.service.d
cat <<EOF >>override.conf
[Service]
# Run the service at lowest priority
LimitNICE=40
EOF
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart php-fpm-site1-example.com
# Resource enforcement
All cgroup service directives apply to PHP-FPM workers, including blkio IO throttling. To set a 2 MB/s write throttle on all PHP-FPM tasks use blkio,writebw or throttle IOPS use the "iops" equivalent, blkio,writeiops:
EditDomain -c cgroup,writebw=2 domain.com
# Apply the min of blkio,writ.ebw/blkio,writeiops
# Both are equivalent assuming 4 KB blocks
EditDomain -c cgroup,writebw=2 -c blkio,writeiops=512 domain.com
Memory ceilings likewise may be set via cgroup,memory.
# Set ceiling of 512 MB for all processes
EditDomain -c cgroup,memory=512 domain.com
IO and CPU weighting may be set via ioweight and cpuweight respectively. ioweight requires usage of the CFQ/BFQ IO elevators.
# Default weight is 100
# Halve IO priority, double CPU priority
EditDomain -c cgroup,ioweight=50 -c cgroup,cpuweight=200 domain.com
See Resource enforcement.md for further details.
WARNING
Setting limits artificially low may create a connection backlog that can prevent consume more system resources than it strives to prevent. Resource limits should be used to prevent egregious abuse, not set firm boundaries based on average daily usage.
# PHP configuration
# Override precedence
ApisCP uses a composition filesystem called BoxFS that allows files inheritance from lower levels and remain on these levels until changed. Once changed, these files copy upward to the account layer. Utilizing this approach, files can be shared upward or templated out to sites.
FILESYSTEMTEMPLATE/siteinfo/etc/php.iniis the base configuration that may be edited by Site Administrators and copied up to their respective account layer.FILESYSTEMTEMPLATE/siteinfo/etc/phpXX.dis a version-specific configuration directory also editable that follows propagation rules.siteXX/fst/etc/php-fpm.d/sites/may not be edited directly and instead relies on inclusion offpm-config-custom.blade.phptemplate. Anyphp_admin_value/php_admin_flagdirective trumps all other matching directive settings.- Site Administrators can apply additional directives in
siteXX/etc/php-fpm.d/that apply to all pools of the site. Must end in .conf and follow PHP-FPM pool directives. .user.iniin each document root allows for additional configuration. This configuration is cached for 300 seconds peruser_ini.cache_ttl.
The following table summarizes inheritance behavior for PHP directives. All locations follow debugging path conventions. Unless marked atypical, configuration follows normal DIRECTIVE=VALUE syntax. See corresponding section for atypical configuration. DOCROOT refers to the document root for the given HTTP resource.
| Location | Editable By | Atypical | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
FST/siteinfo/etc/php.ini | admin | System-wide configuration. Reload fsmount after edit. | |
siteXX/fst/etc/php.ini | admin, site | Copy-up from FST. Requires chown for site edit. | |
siteXX/fst/etc/php-fpm.d/sites | admin, site | X | Service configuration. Cannot override php_admin directives. |
resources/templates/apache/php/partials | admin | X | Service templates. Intended for creation-time configuration. Overrides php_admin. |
siteXX/info/php-policy.xml | admin | X | Policy Maps. Mixed configuration. Can override php_admin if templated. |
DOCROOT/.user.ini | site | User overrides. 5 minute reload interval. Cannot override php_admin. |
# System-wide configuration
System-wide changes may be made to /home/virtual/FILESYSTEMTEMPLATE/siteinfo/etc/php.ini. In single-mount installations, this is linked directly to /etc/php.ini. Once edited, layer cache must be flushed upward.
systemctl reload fsmount
systemctl restart php-fpm
This fails if a site has modified /etc/php.ini within their account root (copy-up semantics of BoxFS). In such situations, an override may be applied either in /home/virtual/FILESYSTEMTEMPLATE/siteinfo/etc/phpXX.d/file.ini or by overriding the PHP-FPM service template. When applied in etc/phpXX.d/, a site owner may remove or edit the file from the account. For a permanent, uneditable solution, see Site templates below.
Any changes should be located at the end of php.ini so as not to conflict with base directives (opens new window) block applied by ApisCP.
Last instance of a directive always wins in php.ini.
WARNING
/etc/phpXX.d is not the same as /home/virtual/FILESYSTEMTEMPLATE/siteinfo/etc/phpXX.d. Files placed in /etc/phpXX.d are not propagated like in /etc/php.ini.
# Service configuration
Next layer of customization is in the pool or systemd service declaration. Pool configuration is located in siteXX/fst/etc/php-fpm.d/sites/ where each configuration is named after the pool. These files may not be directly edited by Site Administrators and are regenerated from template. Files in siteXX/fst/etc/php-fpm.d/ may be edited by Site Administrators.
php_value and php_flag allows these values to be overrode. php_admin_value and php_admin_flag disallow override.
For example, in siteXX/fst/etc/php-fpm.d/memory.conf
php_value[upload_max_filesize] = 64m
php_value[post_max_size] = 64m
Then restart the pool, systemctl restart php-fpm-siteXX
php_admin immutability
Any value marked as php_admin_value or php_admin_flag may not be reset or changed once set. Use fpm-config-custom.blade.php below to update.
# Service templates
Customizations are applied inline to all PHP-FPM pools defined in sites/ if an override exists in config/custom/resources/templates/apache/php/partials/fpm-config-custom.blade.php:
mkdir -p /usr/local/apnscp/config/custom/resources/templates/apache/php/partials/
cat <<EOF >> /usr/local/apnscp/config/custom/resources/templates/apache/php/partials/fpm-config-custom.blade.php
; Note, this is better serviced by cgroup,memory resource enforcement
php_admin_value[memory_limit] = 384m
php_value[upload_max_filesize] = 64m
php_value[post_max_size] = 64m
; Load redis.so from /usr/lib64/<ZENDAPIVERSION>
; When installing modules using Bootstrapper, this is done automatically
php_value[extension] = redis
EOF
Once set, rebuild PHP-FPM for all sites:
EditDomain --reconfig --all
Updating configuration first time
ApisCP compiles configuration on each start to provide the best possible performance. When creating resource overrides in config/custom/resources/view or config/custom/resources/templates the first time restart ApisCP so it knows to look in these directories. Prior to making this change, these locations are compiled out on boot.
systemctl restart apiscp
# User overrides
PHP-FPM uses .user.ini in each document root to set PHP configuration at runtime.
Configuration in PHP-FPM is assignment-based, similar to php.ini, rather than directive. Paths are jailed and respect the synthetic root layout. For example,
.htaccess
php_value auto_prepend_file /home/virtual/site12/fst/var/www/html/heading.php
.user.ini
auto_prepend_file = /var/www/html/heading.php
PHP-FPM caches per-directory .user.ini files. By default the duration is 300 seconds (5 minutes). This can be altered by adding a FPM configuration to /etc/php-fpm.d/file.conf or by overriding the PHP-FPM template in templates/apache/php/.
Then restart the affected pool, systemctl restart php-fpm-siteXX where siteXX is the site marker or do an en masse restart with systemctl restart php-fpm.
Since v3.1.38, directives are migrated automatically for all known domain/subdomain parent document roots when a site is switched between jail/non-jail mode. php:migrate-directives(string $host, string $path = '', string $from) provides a migration interface for directives behind a subdirectory.
Directives may be applied pool-wide by the Site Administrator by creating a new file in /etc/php-fpm.d/, by editing /etc/php.ini directly, or creating a drop-in in /etc/phpXX.d/. Pools may be restarted by the Site Administrator in Web > PHP Pools.
# Masquerading other file types as PHP
Don't do this. Use a dispatcher via .htaccess to funnel all requests to emulate desired behavior. Should prevailing wisdom fail, add the following to the .htaccess to map .html and .htm to PHP-FPM:
<Files ~ "\.html?$">
ProxyFCGISetEnvIf "reqenv('VPATH') =~ m|^/home/virtual/[^/]+/fst(/.++)$|" SCRIPT_FILENAME "$1/%{reqenv:SCRIPT_NAME}"
SetHandler "%{env:PHP_HANDLER}"
</Files>
Next override security.limit_extensions (opens new window) in /etc/php-fpm.d/:
security.limit_extensions=.php .phar .html .htm
Then restart the affected pool, systemctl restart php-fpm-siteXX where siteXX is the site marker or do an en masse restart with systemctl restart php-fpm.
# /tmp location
New in 3.2.25
PrivateTmp (opens new window) is enabled by default for PHP-FPM sites. On-disk sessions, temporary files, and file uploads are stored on a temporary RAM disk under /tmp without the ability to see other files in /tmp, run programs directly, elevate permissions, or create block devices (mount -o noexec,nosuid,nodev). Files created here receive a boost in I/O speed, but memory is a limited resource. Larger sites that receive significant file uploads or make use of tempnam(), tmpfile() calls in PHP can exhaust available storage.
These sites may be relocated to the account filesystem root in /home/virtual/siteXX/fst/tmp. On-disk sessions, temporary files, and file uploads will be stored on within the account and likewise be counted toward the account filesystem quota. Set privatetmp: false in the policy map. Once modified, run EditDomain --reconfig domain.com.
Making this change will also grant the PHP-FPM process access to view files within /tmp for that account as well as allow others on the account to interact with those files.
This setting may be altered globally in config.ini under [httpd] => fpm_privatetmp. Default value is true, to enable PrivateTmp usage.
# HTTP configuration
# PHP-FPM timeout
The web server expects a request to complete within 60 seconds. Any request outside this window will return a 504 Gateway Timeout response. Alter the system-wide configuration in /etc/httpd/conf/httpd-custom.conf by setting ProxyTimeout 180 to raise the limit to 3 minutes. Proxy timeout may be adjusted on a per-site basis by creating a file named custom in /etc/httpd/conf/siteXX with the same directive. When overriding per-site, be sure to rebuild the configuration:
# Get XX via get_site_id domain.com
echo 'ProxyTimeout 180' >> /etc/httpd/conf/siteXX/custom
htrebuild
systemctl reload httpd
Granular per-proxy configuration is covered in "Apache proxy configuration" below.
# Worker limits
Apache uses an Event MPM, which consists of 1 or more processes (called "children") consisting of 1 or more threads. By default, each child consists of 20 threads. THREADS x CHILDREN gives the maximum number of concurrent connections. See Apache.md for more information on configuration.
Each process does not communicate with one another. These processes operate independently. Configurations specified below therefore apply per child. For example, setting a "max" number of connections to a PHP-FPM worker as 2 does not restrict at most 2 concurrent connections to a site, but at most 2 concurrent connections in that child process to the PHP-FPM backend. The true limit is MAX X CHILDREN. Keepalives may result in successive requests binding to the former child instead of distributing requests evenly between all children.
PHP-FPM utilizes "ondemand" as its process manager to spawn PHP workers on demand and likewise sleep after extended idle periods (default: 60 seconds). ondemand imposes a minimum backlog value of 511 connections, which means in the event a PHP-FPM worker cannot furnish a request immediately, up to 511 connections may linger in Apache pending acknowledgement by PHP-FPM before further requests are rejected. If the pending connection balance exceeds ServerLimit in Apache, then no further requests may be made to the server, including to static resources.
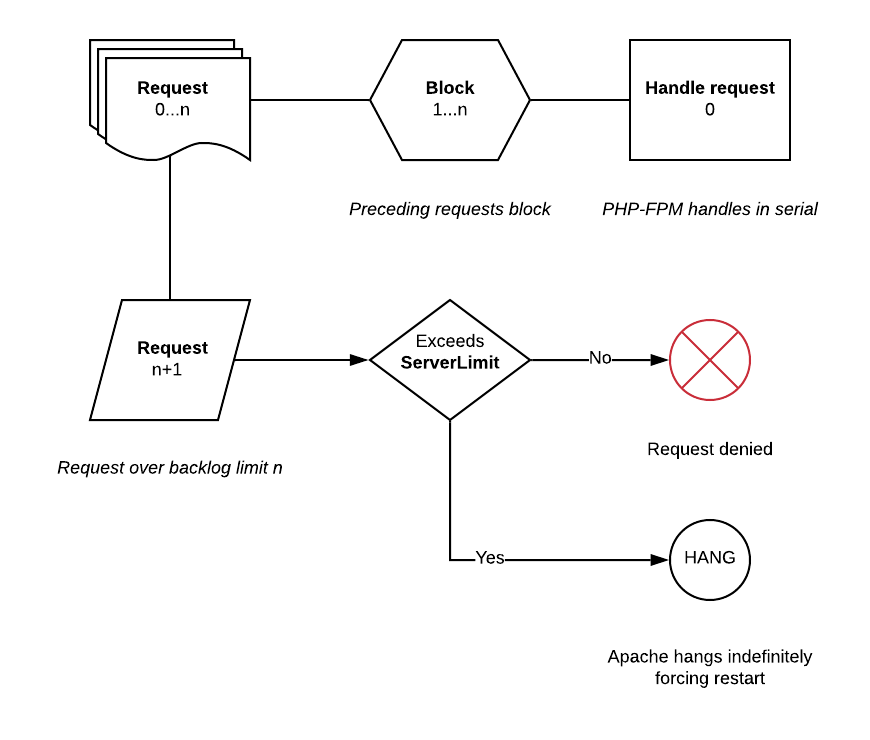
When a PHP-FPM worker spawns, it clones the parent memory, which provides the bare essentials to begin furnishing a request. Cloning takes very little time (< 50 ms) after which point it will accept the request over its socket. If a request is blocked, the request cannot be accepted over socket. Tuning is intended to prevent monopolization of available connection slots that PHP-FPM would not adequately restrict. In high throughput environments, these numbers should be raised.
Set a maximum number of connections to the PHP-FPM socket and set an accept() timeout to prevent blocked requests from piling up and thus monopolizing available connection slots in Apache. The following directives in siteXX/custom set a worker limit of 5 connections per server with a 10 second delay in accept(). The total connection backlog is thus 5 X SERVERS or in a default configuration with 20 ThreadsPerChild 25% of the available connection slots.
<Proxy "fcgi://localhost" max=5 acquire=10s>
</Proxy>
A template is provided that permits overriding proxy settings via resources/templates/apache/php/partials/proxy-settings.blade.php. See Customizing.md for tips on overriding this template. Any directive permitted within a <Proxy> directive may be used in proxy-settings.blade.php. For example, to raise the total connection time to 600 seconds for a request:
ProxySet timeout=600s
After making changes, edit all domains that use PHP-FPM to effect changes.
EditDomain --all
# Multiversion PHP
Multiversion comes in two flavors, native (also called "multiPHP") and Remi, named after the eponymous author that maintains the Remi build system.
# Native builds
ApisCP ships with 1 PHP release for simplicity, but can support multiple versions as necessary. Additional versions may be built using Bootstrapper. A Scope is provided, php.multi, that facilitates building new versions.
# Add additional compile-time flags to 7.4 and build it
cpcmd scope:set cp.bootstrapper php74_build_flags "--with-password-argon2"
# Add PHP 7.4 support
cpcmd scope:set php.multi 7.4
# Remove PHP 7.4
cpcmd scope:set php.multi '[7.4:false]'
All native multiPHP builds are located in /.socket/php/multiphp/native. OPCache is configured automatically.
# Automatic builds/updates
New in 3.2.6
php_multiphp is a Bootstrapper setting that allows automated builds at install and updates during monthly platform checks. Versions should be defined as a list of MAJOR.MINOR versions; MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH works but would never update past initial install.
cpcmd scope:set cp.bootstrapper php_multiphp '[5.6,7.2]'
upcp -sb php/multiphp
# Similar to above, but add 7.1
cpcmd scope:set php.multi '[5.6,7.1]'
# Reports 5.6, 7.1, and 7.2
cpcmd scope:get php.multi
# Remove PHP 7.2
cpcmd scope:set php.multi '[7.2:false]'
# Report active multiPHP versions 5.6, 7.1
cpcmd scope:get php.multi
The latest version of 5.6 and 7.2 would build as multiPHP releases. Any extensions defined either globally (pecl_extensions) or per-version (pecl_phpXX) are also installed as needed.
# Installing modules
Modules may be installed as one would normally expect with regular PHP-FPM. The only difference is the presence of php_version that must be explicitly set.
To install imagick off PECL for PHP 7.4,
upcp -sb --var=pecl_extensions=igbinary --var=php_version=7.4 php/install-extensions
Likewise pecl_php74 could be set as a list with ['igbinary'] to automatically build for PHP 7.4:
cpcmd scope:set cp.bootstrapper pecl_php74 '[igbinary]'
upcp -sb --var=php_version=7.4 php/install-extensions
# Remi builds
For easier package-based multiPHP management, ApisCP includes support for Remi PHP (opens new window). If installing on CentOS or RedHat 8, change "7" to "8".
yum install http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-$(rpm -E '%{rhel}').rpm
Then to install say PHP 7.4 with ionCube loader, MySQL, OPCache PECL:
yum install -y php74-php-fpm php74-php-ioncube-loader php74-php-pecl-mysql php74-php-opcache
# Installing modules
Remi does not support manual installation of modules. Use packages provided through the public RPM repository. yum list 'php*-pecl-*' will give an indication of packages available for install.
# Adding non-PHP Remi packages
Additional packages may be installed first from Remi, then replicated into the FST. Yum Synchronizer ("Synchronizer") located in bin/scripts/yum-post.php provides a set of tools to manage RPM replication into FST.
# Install "vips" package from Remi
yum install -y vips
# Query "vips" dependencies
cd /usr/local/apnscp
./bin/scripts/yum-post.php depends vips
# WARNING : CLI\Yum\Synchronizer\Depends::run(): Package `vips' is not resolved. Install the following dependencies to resolve: ilmbase, OpenEXR-libs, ImageMagick6-libs, cfitsio, libexif, fftw-libs-double, gdk-pixbuf2, libgsf, hdf5, matio, openslide, orc, pango, poppler-glib, librsvg2, vips, libwebp7
# Install vips into siteinfo. "-d" installs dependencies as well
./bin/scripts/yum-post.php install -d vips siteinfo
-d calculates dependencies necessary to satisfy operation and installs those packages into the named service layer. When mixing packages between different services that may be satisfied by a union of service layers, it is permissible to omit "-d". Installing packages without installing the dependencies, however, may cause PHP or any binary to fail to load.
# Solving dependencies
yum-post.php includes a dependency solver.
Install the ImageMagick extension from PECL, then attempt to load PHP-FPM from the account, it will fail:
yum install -y php72-php-pecl-imagick
su apis.com
# Try loading PHP-FPM, dependencies will prevent it from starting
/usr/bin/scl enable php72 -- php-fpm --nodaemonize --fpm-config=/etc/php-fpm.d/sites/apis.com.conf
# [09-Jan-2020 13:17:36] NOTICE: PHP message: PHP Warning: PHP Startup: Unable to load dynamic library 'imagick.so' (tried: /opt/remi/php72/root/usr/lib64/php/modules/imagick.so (libharfbuzz.so.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory), /opt/remi/php72/root/usr/lib64/php/modules/imagick.so.so (/opt/remi/php72/root/usr/lib64/php/modules/imagick.so.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory)) in Unknown on line 0
Exit out of the shell, solve the dependencies, then try again:
# Exit current su apis.com session
exit
rpm -qf /usr/lib64/libharfbuzz.so.0
# Package is libharfbuzz. Install it plus all dependencies (-d)
/usr/local/apnscp/bin/scripts/yum-post.php install -d libharfbuzz siteinfo
su apis.com
# Try loading PHP-FPM again... rinse and repeat until it works
Do not attempt to install a module directly; it is already relocated. Once satisfied, you may run into permission issues if PHP-FPM runs as an unprivileged system user ("apache") rather than the account owner. su -s /bin/bash -G ADMINUSER apache would setup a similar environment to systemd prior to launch.
# Native vs Remi
Remi is an easier system to manage when juggling a variety of PHP versions, but it comes at some cost to performance and potential dependency management.
- Modular builds are slower than monolithic both in startup time and run time.
- Generalized builds are unable to target system-specific optimizations. WordPress throughput for example drops 9.38% (16.13 req/sec vs 17.80 req/sec) when using Remi builds.
- Remi is not officially supported by Apis Networks for support. PHP bundled with ApisCP is built with features to address nearly all hosting inquiries over the last 15 years.
- Remi builds do not provide configuration adjustments to Site Administrators.
- Each PHP release may have different library requirements.
yum-post.php dependswill do its best to resolve these for you. After setup, verify it works correctly in an account (su domain.com) by runningscl enable phpXX -- php -r 'phpinfo();' > /dev/nullto attempt to load all extensions. This will pull in PHP extensions and hopefully provide some hint at what - if anything - is missing.
# Switching versions
# API
New in 3.2.18
Use cpcmd -d domain.com php:pool-set-version $VERSION to set the pool version for a site. All versions can be listed by cpcmd -d domain.com php:pool-versions.
Likewise end-users may adjust their pools via Web > PHP Pools. Pools may be restricted using a policy map.
# Manual
Override precedence
Manually setting PHP versions takes precedence over the API. This may be useful to lock a site to use a specific pool.
# Native
In /etc/systemd/system, create a directory named after the pool and suffixed with ".d". Pools are named php-fpm-siteXX-NAME. For example, to override pool named apis.com on site1, create a directory named php-fpm-site1-apis.com.d/ and a file named "override.conf".
systemctl edit php-fpm-site1-apis.com is equivalent to the above operation.
[Service]
# The next line overrides the previously inherited ExecStart
ExecStart=
# DO NOT surround in quotes, it would be treated as a literal if so
ExecStart=/.socket/php/multiphp/native/7.4/sbin/php-fpm --nodaemonize --fpm-config=/etc/php-fpm.d/sites/apis.com.conf
Then restart the service,
systemctl restart php-fpm-site1-apis.com
# Remi
In /etc/systemd/system, create a directory named after the pool and suffixed with ".d". Pools are named php-fpm-siteXX-NAME. For example, to override pool named apis.com on site1, create a directory named php-fpm-site1-apis.com.d/ and a file named "override.conf".
systemctl edit php-fpm-site1-apis.com is equivalent to the above operation.
[Service]
# The next line overrides the previously inherited ExecStart
ExecStart=
# DO NOT surround in quotes, it would be treated as a literal if so
ExecStart=/usr/bin/scl enable php74 -- php-fpm --daemonize --fpm-config=/etc/php-fpm.d/sites/apis.com.conf
Then restart the service,
systemctl restart php-fpm-site1-apis.com
This is very similar to native with a few key differences:
- SCL is used to shim a new path, "php-fpm" is picked up in this shimmed path. /usr/sbin/php-fpm would be incorrect.
- An empty
ExecStart=clears any previous ExecStart directives. Without this, ExecStart would be appended to the inherited ExecStart= command that starts PHP-FPM. --nodaemonizechanges to--daemonizeto ensure systemd picks up the scl to php-fpm process image change.
PHP runtimes are located in php<MAJOR><MINOR>-runtime packages. php<MAJOR><MINOR> is a dummy package that pulls in dependency packages, including runtime.
SCL collection configuration is defined in /etc/scl/conf. Remi PHP versions are named php<MAJOR><MINOR>.
# Policy maps
New in 3.2.18
A policy map remembers what PHP version is assigned to a given pool or account as well as setting several important parameters. Each policy map is generated from a template and saved to the account under siteXX/info/php-policy.yml. When hand-editing a policy, run EditDomain --reconfig siteXX to regenerate its configuration as well as restart PHP-FPM.
☝ See master branch (opens new window) for latest policy template.
global:
# defaults to system version
# Bootstrapper value: system_php_version
version:
# Max PHP-FPM workers
# PHP-FPM value: pm.max_children
workers: {{ max(NPROC+2, 5) }}
# Max idle duration before a PHP-FPM worker quits
# PHP-FPM value: pm.process_idle_timeout
idle_timeout: 60s
# Max threads dedicated per server for queuing
# Apache value: <Proxy max=n>
threads: 3
# Max backlog
# PHP-FPM value: listen.backlog
backlog: 30
# Connection timeout
# Apache value: <Proxy acquire=n>
connect: 5s
# All php_admin settings - cannot be overrode
php_settings:
# Maximum memory *per* PHP-FPM worker (keep low!)
# PHP value: memory_limit
memory_limit: {{ (int)min(\Opcenter\System\Memory::stats()['memtotal']/1024*0.15,384) }}M
# Boolean. Set PrivateTmp=true in PHP-FPM systemd unit file. PrivateTmp=true puts the account
# under system /tmp, which is backed by tmpfs. This boosts performance for session reads,
# temporary file storage, and prevents execution of files - but an active site can fill /tmp,
# which has limited storage.
# When unset defaults to [httpd] => fpm_privatetmp
privatetmp:
pools:
# Per-pool configuration is not supported yet!
# "mydomain.com":
# workers: 5
# version: null or specific version
# List of versions to disallow
blacklist:
# - 5.6
# - 7.0
# List of versions to allow
# Omit to allow all versions
whitelist:
As this is a Blade template, it's also possible to template the configuration.
global:
# Set default PHP interpreter to 5.6 for legacy plans
@if ($svc->getServiceValue('siteinfo', 'plan') === 'legacy')
version: '5.6'
@else
version: '8.0'
@endif
workers: {{ max(NPROC+2, 5) }}
Note the additional spacing after each conditional statement. This is a formatting peculiarity of Blade that joins the following line on compilation.
# Policy map API
New in v3.2.37
Policies may be viewed per-site but only managed administratively.
php:pool_get_policy(string $var, string $pool = null, string $default = null)
php:pool_set_policy(string $anything, string $var, $val, string $pool = null): bool
Working with the above example to get memory_limit, an administratively set value for the pool on site1, the following command is used:
cpcmd -d site1 php:pool-get-policy php_settings.memory_limit
# Returns 384M
Values are determined by the union between local pool settings in siteXX/info/php-policy.yml and defaults in resources/templates/apache/php/policy.blade.php (note: resources follow config/custom/ override rules in Customizing.md). Values in php-policy.yml always have precedence. Values named within the named pools group have precedence over the global section.
Next, to change this value for all pools within site1, use php:pool-set-policy. EditDomain is automatically enqueued.
cpcmd php:pool-set-policy site1 php_settings.memory_limit 1G
INFO : PHP pool settings batched to background
----------------------------------------
MESSAGE SUMMARY
Reporter level: OK
INFO: PHP pool settings batched to background
----------------------------------------
$anything may be a site, domain, or invoice to change a group of related domains.
To change a specific pool, specify the pool parameter. This value takes precedence over global settings.
cpcmd php:pool-set-policy site1 php_settings.memory_limit 2G benchmark.test
cpcmd php:pool-set-policy site1 php_settings.memory_limit 512M
# Pool named "benchmark.test" has a 2G limit, all other named pools are 512 MB
# Composer
# Updating
Run php/composer with composer_keep_updates=true to force a manual update of Composer. Composer may be periodically updated every platform scrub by setting this value in apnscp-vars-runtime.yml. A Scope is provided to make this easier.
# Update one-time
env BSARGS="--extra-vars=composer_keep_updated=true" upcp -sb php/composer
# Keep updated during scrubs
cpcmd scope:set php.composer-autoupdate true
# Troubleshooting
# Pool fails to start
Pools use socket activation to start. When activity comes across /run/php-fpm/siteXX-pool-name.socket, the corresponding service, php-fpm-siteXX-pool-name is started using systemd. systemd has a hold-off period that marks a pool as failed if more than 3 restarts occur within a 15 second interval. Restrictions are in place to avoid unintended denial of service attacks. systemd does not provide a means to restart these pools once deactivated either, requiring manual intervention within the panel to restart.
Validate the concern that caused the pool not to start.
journalctl -n20 -u php-fpm-siteXX-domain.com
# Look for timestamps of failures, e.g.
# Nov 22 20:11:59 test3.apisnetworks.com php-fpm[7199]: [22-Nov-2020 20:11:59] WARNING: Nothing matches the include pattern '/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf' from /etc/php-fpm.d/sites/apisnetworks.test.conf at line 53.
# Nov 22 20:11:59 test3.apisnetworks.com php-fpm[7199]: [22-Nov-2020 20:11:59] ERROR: Unable to write to the PID file.: Disk quota exceeded (122)
# Nov 22 20:11:59 test3.apisnetworks.com php-fpm[7199]: [22-Nov-2020 20:11:59] ERROR: FPM initialization failed
# Nov 22 20:11:59 test3.apisnetworks.com systemd[1]: php-fpm-site193-apisnetworks.test.service holdoff time over, scheduling restart.
# Nov 22 20:11:59 test3.apisnetworks.com systemd[1]: Stopped PHP worker for site193 - apisnetworks.test.
# Nov 22 20:11:59 test3.apisnetworks.com systemd[1]: start request repeated too quickly for php-fpm-site193-apisnetworks.test.service
# Nov 22 20:11:59 test3.apisnetworks.com systemd[1]: Failed to start PHP worker for site193 - apisnetworks.test.
# Nov 22 20:11:59 test3.apisnetworks.com systemd[1]: Unit php-fpm-site193-apisnetworks.test.service entered failed state.
# Nov 22 20:11:59 test3.apisnetworks.com systemd[1]: php-fpm-site193-apisnetworks.test.service failed.
Correct the underlying cause to remedy the problem. In this case increase disk quota: EditDomain -c diskquota,quota=10000 -D apisnetworks.test.
Scroll up
PHP-FPM will attempt to restart 3 times logging each failure. Because of this behavior the root cause may not be immediately apparent in the last 13 lines (4 diagnostic lines per failure + 1 final failure).
# Verifying pool socket status
systemctl list-sockets --state=failed php-fpm* displays all failed sockets, which can be due to the PHP-FPM service failing to start or socket failing to start.
journalctl -n20 -u php-fpm-siteXX-NAME.service from the ACTIVATES column will give more information up to the last 20 lines as noted above in "Pool fails to start".

