New in 3.2.48
mod_shield is an advanced bean counter that tracks HTTP requests, status codes, and response times over a large window to discriminate against malicious actors. When an IP address exceeds the point threshold within the duration, a configurable response is immediately returned and information is emitted from syslog to fail2ban, which allows Rampart to respond to to the incident. Additionally a file named /tmp/dos-IP is created marking the event.
Requests are tracked by two methods: same URI and same site. An IP which exceeds either limit is blocked in the same manner.
# Configuration
apache.shield Scope manages mod_shield parameters. This Scope interacts with /etc/httpd/conf.d/shield.conf and adds a 2 minute delay to reloading HTTP configuration.
Apache directives are parenthesized for each named directive.
# Page tracking
Same URI tracks the full URI provided to Apache. When canonical (DOSCanonical on|off) is enabled (default), query strings are truncated from the request: /foo is the same as /foo?bar=baz and /foo?quu=qux&bar=baz.
page-count (DOSPageCount AMOUNT) and page-interval (DOSPageInterval SECONDS) control hit count and window. Recommended settings are a low interval and count greater than interval.
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield page-count 20
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield page-interval 5
Above triggers protection if more than a score of 20 is reached on the same URI within 5 seconds.
# Page deadlines
Scoring may be adjusted if a response takes longer than n seconds using shield-deadline (DOSPageDeadline DURATION SCORE|off). Score may be any whole number, positive or negative. Deadlines are additive. Each page request always generates 1 point. Setting off disables this feature.
# Any page that loads below 250 ms receives a -2 score
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-deadline 0 -2
# Ignore any page that loads under 500 ms
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-deadline 0.250 0
# Any page that loads above 500 ms is scored 1 extra point
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-deadline 0.500 1
# Alternative form
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-deadline '[0:-2, 0.250:0, 0.500:1]'
# Cancel 250 ms score
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-deadline 0.250 null
# Reset scoring to default
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-deadline null
# Disable all deadline scoring
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-deadline false
# Accepted for interoperability
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-deadline off
# Site tracking
Site tracking ignores URI distinctions and looks at all requests originating from an IP against a HTTP hostname. /foo and /bar both accumulate hits.
site-count (DOSSiteCount AMOUNT) and site-interval (DOSSiteInterval SECONDS) control hit count and window. This ratio must be higher than page-based accumulation. Setting a high interval or low count will trigger false positives at a much higher rate, especially in plugin-dependent Web Applications, such as WordPress.
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield site-count 300
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield site-interval 2
Above triggers protection if more than 300 requests are made within 2 seconds.
# Status penalties
Scoring may be adjusted for any HTTP response code, such as a 304, 403, 404 or even a custom status like 418 I'm a teapot (opens new window) using shield-status (DOSPageStatus STATUS SCORE|off).. Status codes are evaluated from the final response in a processing pipeline.
# Add 50 points if HTTP status code is 418
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-status 418 50
# Remove penalty for 302, "0" works as well
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-status 302 false
# Add a -5 point adjustment for 204, not modified
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-status 204 -5
# Reset scoring to default
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-status null
# Disable all deadline scoring
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-status false
# Accepted for interoperability
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-status off
For sites that are composed with best practices in mind, 404 and non-2xx status codes are rare; thus, default status penalties are optimal.
# Status handler
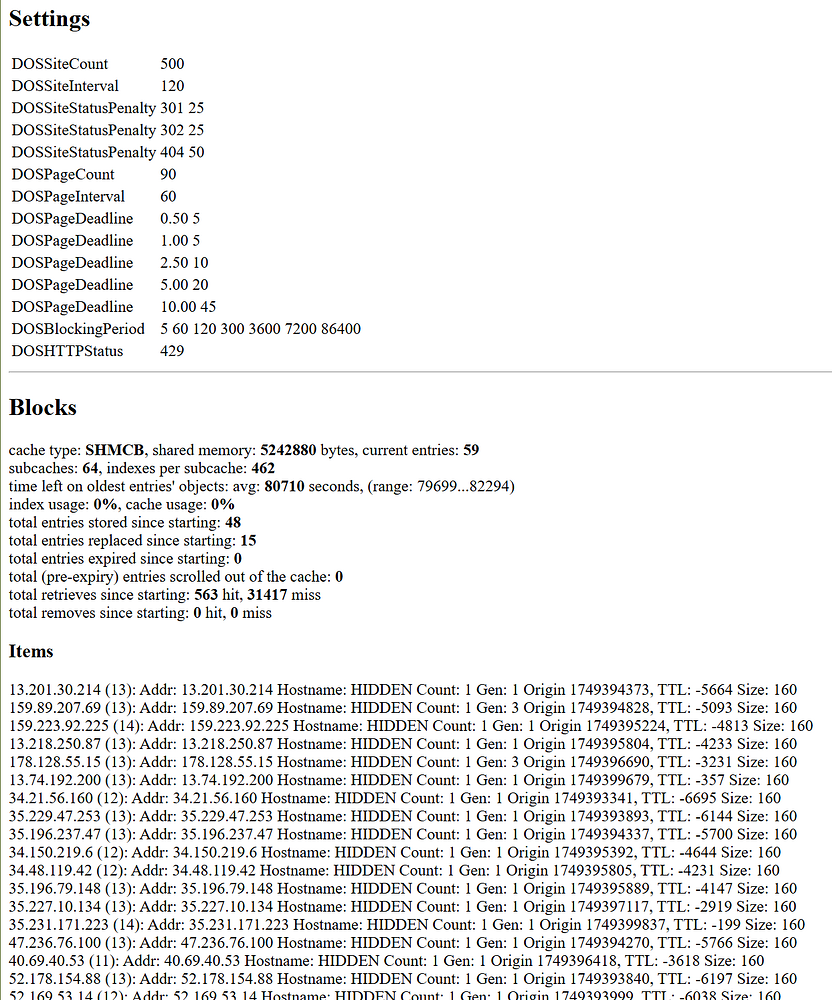
A separate status handler named shield-status is available. Settings, active blocks, and individual counters for same-page and site resources are provided.
It may be activated with the following directives in /etc/httpd/conf/httpd-custom.conf:
<Location /shield>
SetHandler shield-handler
# It's a good idea to limit traffic to your IP.
# Accepts CIDR-style
Require ip your.ip.address
</Location>
Whitelist
HTTP blocks occur early in the pipeline before any overrides or per-directory processing to reduce CPU strain. It's a good idea to also whitelist these IP addresses that are permitted to view the status overview in case they too get blocked.
# Never block any address between 1.2.3.1 and 1.2.3.255
cpcmd scope:set apache.shield-whitelist 1.2.3.1/24
# Disabling per site
Shield may be disabled directly with DOSEnabled off or indirectly by setting apache,shield=0 for the site.
# Direct disablement
Create a file named custom in /etc/httpd/conf/siteXX where siteXX is the site ID for the domain. get_site_id domain.com from command-line will help you locate this value. Within custom add:
DOSEnabled off
Then rebuild and reload, htrebuild && systemctl reload httpd.
# Indirect
EditDomain -c shield,shield=0 domain.com
# Empirical estimates
Running a site through webpagetest.org or using DevTools (opens new window) to see the average number of subrequests per page view can help you estimate a good baseline for your site. An ideal setting allows typical usage while disabling atypical extremes: bots don't adhere to netiquette when brute-forcing credentials. Some protection is necessary.
# Block metadata
Whenever a block occurs, a separate file is created in /tmp with the blocked address. File format is: PID<NL>[site|page] GENERATION COUNT HOSTNAME ORIGIN-TIMESTAMP GROWTH-RATE<NL>URI. GROWTH-RATE - points per second - is the scoring rate per second accumulated defined as COUNT/(NOW - ORIGIN-TIMESTAMP).
# Filtering individual resources
mod_shield is context-aware using Apache directives. For example, Shield ships with a filter to restrict POST attempts to xmlrpc.php and wp-login.php. cpcmd config:set apache.shield-wordpress-filter true enables this filter with a very stringent post rate of 3 attempts in 2 seconds.
As an example, the following rule applies to files named "wp-login.php", glob is quicker than regular expression patterns by a factor of 5-10x! If the request method isn't a POST, disable bean counting. If more than 3 POST attempts to the same resource occur within a 2 second interval, then return a DOSHTTPStatus response (429 Too Many Requests) and log the message via syslog to /var/log/messages. fail2ban will pick up the request and place the IP address into the temporary ban list.
# Block wp-login brute-force attempts
<Files "wp-login.php">
<If "%{REQUEST_METHOD} != 'POST'">
DOSEnabled off
</If>
DOSPageCount 3
DOSPageInterval 2
</Files>
# Customizing
Copy resources/templates/rampart/shield/wordpress-filter.blade.php to config/custom/resources/templates/rampart/shield/wordpress-filter.blade.php creating parent directory structure as necessary:
cd /usr/local/apnscp
install -D -m 644 resources/templates/rampart/shield/wordpress-filter.blade.php config/custom/resources/templates/rampart/shield/wordpress-filter.blade.php
First time use requires regeneration of cache or restart of ApisCP,
cd /usr/local/apnscp
./artisan config:clear
# Adjusting cache size
Shield implements a cyclic shared buffer - default 512 KB - for each tracking criteria (site, page, and blocks). Each record is 176 bytes allowing for 2,978 unique entries that covers approximately 25 unique requests/second over a 2 minute tracking window.
Cache backend and size are both modifiable. Redis (opens new window) and Memcached (opens new window) may be used to share hit data across servers. Latency spikes during locking may occur with either backend.
cpcmd config:set apache.shield cache-size N will adjust the cache size. If no unit is specified, KB is assumed. If a cache provider other than shmcb is active, this setting has no effect.
Cache size can also be set directly in httpd-custom.conf.
# Resize cache size to 1 MB
DOSCache shmcb:none(1048576)
# Proxy Compatibility
Shield may pierce a downstream proxy applying the block directly against the client IP. IPs blocked in this manner cannot be blocked by firewall but will continue to report an error code without further request processing.
# Cloudflare
mod_cloudflare updates the IP address of a request in ap_hook_post_read_request() before ap_hook_access_checker(); thus, at evaluation rec->useragent_ip reflects the upstream IP.
# Others
mod_remoteip (opens new window) defines a set of trusted downstream proxies for which the forwarded IP is truthful. Support may be added in httpd-custom.conf.
LoadModule remoteip_module modules/mod_remoteip.so
# Header downstream sends connecting IP
RemoteIPHeader X-Client-IP
RemoteIPTrustedProxy 4.4.4.4
Trusting internal network addresses
RemoteIPTrustedProxy discards any internal network ranges (10/8, 172.16/12, 192.168/16, 169.254/16, 127/8 or outside IPv6 public 2000::/3 block). Specify RemoteIPInternalProxy (opens new window) instead if your network topology includes internal networks also subject to filtering.
